CPM® MagnaCut
DATA SHEET
Typical Composition
| C | Cr | V | Mo | Nb | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.15% | 10.7% | 4.00% | 2.00% | 2.00% | 0.20% |
CPM® MagnaCut is a unique powder metallurgy stainless tool steel with a design which eliminates chromium carbide in the heat treated microstructure. An excellent combination of toughness and wear resistance is achieved by having only small, high hardness, vanadium and niobium carbides, giving CPM® MagnaCut properties similar to non-stainless steel CPM® 4V. Being free from chromium carbide also leads to improved corrosion resistance. This product offers an excellent combination of properties for knives.
For more information visit: Knife Steel Nerds
Typical Applications include long-wearing specialty cutlery, plastic injection and extrusion feed screws and dies, pelletizing equipment, and wear components for food and chemical processing.
Note: These are some typical applications. Your specific application should not be undertaken without independent study and evaluation for suitability.

CPM® MagnaCut
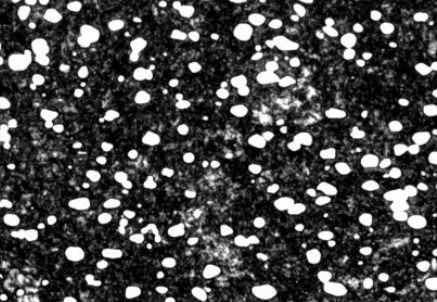
CPM® 154
Carbide Type and Volume
| Vanadium | Niobium | Chromium | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MagnaCut* | 6.5% | 1.5% | 0% | 8.0% |
| CPM® S35VN** | 2.0% | 0.5% | 10.5% | 13.0% |
| CPM® S45VN** | 2.0% | 0.5% | 12.5% | 15.0% |
| 4V* | 8.0% | 0% | 8.0% | |
| S90V* | 9.0% | 13.0% | 22.0% | |
| CPM® 154* | 16.0% | 16.0% |
* Determined by analysis of SEM backscatter micrographs
** Estimated by thermodynamic software
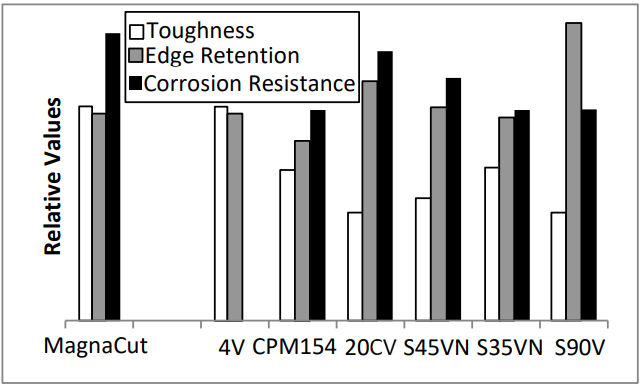
Tool Steel Comparagraph
Physical Properties
Elastic Modules 31 X 10^6 psi (215 GPa)
Density 0.28 lbs./in^3 (7.76 g/cm^3)
Thermal Conductivity
| Temp. | BTU/hr·ft·°F | W/m·°K | cal/cm·s·°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200°F (93°C) | 10.8 | 18.6 | 4.4 × 10−2 |
Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
| °F | °C | in/in/°F | mm/mm/°C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70 – 400 | (20 – 200) | 6.4 × 10−6 | (11.6 × 10−6) |
Mechanical Properties
Toughness
(Longitudinal Charpy C-Notch values converted from ¼-size unnotched specimens)
| Grade | HRC | Toughness (ft-lbs) |
|---|---|---|
| MagnaCut | 62.5 | 38 |
| MagnaCut | 64 | 30 |
| 4V | 62 | 36 |
| CPM® 154 | 60 | 26 |
| S35VN | 61 | 25 |
| S45VN | 61.5 | 19 |
| S90V | 61 | 17 |
| 20CV | 62 | 15 |
The excellent toughness results indicate that CPM® MagnaCut is very resistant to chipping and breaking. In knifemaking, the high toughness makes it especially good for bigger blades. And fine cutting knives can have thinner edges for better cutting ability with reduced risk of chipping.
Edge Retention
(CATRA Testing Relative to 440C)
| Grade | HRC | % |
|---|---|---|
| MagnaCut | 62.5 | 135 |
| S90V | 61.5 | 195 |
| 20CV | 61.5 | 155 |
| S45VN | 61.5 | 140 |
| S35VN | 61 | 130 |
| CPM® 154 | 61 | 120 |
| 440C | 56 | 100 |
The CATRA (Cutlery & Allied Trades Research Association) test machine performs a standard cutting operation and measures the number of silica impregnated cards which are cut. It is considered a measure of relative wear resistance, reported in this table as compared to a 440C standard.
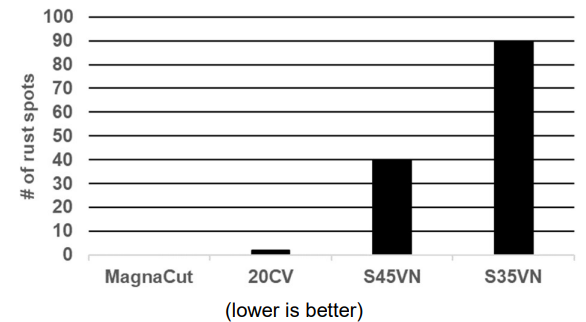
Corrosion Resistance
(1% saltwater spray test for 72 hours)
Thermal Treatments
Forging: 2100°F (1150°C) Do not forge below 1750°F (950°C).
Annealing: Heat to 1650°F (900°C), hold 2 hours, slow cool no faster than 25°F (15°C) per hour to 1100°F (595°C), then furnace cool or cool in still air to room temperature.
Annealed Hardness: About BHN 235.
Stress Relieving
Annealed Parts: Heat to 1100-1300°F (595-705°C), hold 2 hours, then furnace cool or cool in still air.
Hardened Parts: Heat to 25-50°F (15-30°C) below original tempering temperature, hold 2 hours, then furnace cool or cool in still air.
Straightening: Best done warm 400-800°F (200-425°C).
Hardening
Preheat: Heat to 1550-1600°F (845-870°C) Equalize.
Austenitize: 1950-2200°F (1065-1205°C), hold time at temperature as shown in chart. Thick cross-sections and larger pieces may need longer austenitizing time.
Quench: Plate quench, air or positive pressure quench (2 bar minimum) to below 125°F (50°C), or salt or interrupted oil quench to about 1000°F (540°C), then air cool to below 125°F (50°C).
Cold Treatment: A cold treatment may be used after the quench to decrease retained austenite and increase hardness. Tempering before the cold treatment decreases the effectiveness of the cold treatment but also decreases the chance of warping or cracking. A freezer treatment at -10°F (-23°C) has no effect unless performed directly after the quench with no delay.
Temper: Double temper at 300-450°F (150-230°C). Hold for 2 hours minimum each time.
NOTE: Tempering above 750°F (400°C) results in a decrease in corrosion resistance.
Size Change: +0.05 to +0.10% when fully martensitic. The presence of retained austenite may reduce the net growth. When tempering at 300-750°F (150-400°C), freezing treatments may be necessary to minimize retained austenite.
Recommended Heat Treatment:
Austenitize 2050°F (1120°C). Quench to below 125°F (50°C). Double temper at 350°F (175°C) 2 hrs. minimum each temper. Cool to hand warm between tempers. A freeze treatment may be added after the quench.
Aim hardness: 60-63 HRC.
Note: Properties shown throughout this data sheet are typical values. Normal variations in chemistry, size and heat treat conditions may cause deviations from these values.
| Austenitizing – Plate/Oil Quench to Room Temperature | ||||||
| Min Aust Time | 30 min | 25 min | 20 min | 15 min | 10 min | 5 min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temper | 1950°F (1065°C) |
2000°F (1095°C) |
2050°F (1120°C) |
2100°F (1150°C) |
2150°F (1175°C) |
2200°F (1205°C) |
| 300°F (150°C) | 60.5 | 62 | 62.5 | 63 | 63.5 | 63 |
| 350°F (175°C) | 59.5 | 60.5 | 61.5 | 61.5 | 62 | 61.5 |
| 400°F (205°C) | 58.5 | 59.5 | 60 | 60.5 | 60.5 | 60.5 |
| 500°F (260°C) | 57.5 | 58.5 | 58.5 | 59 | 60 | 59.5 |
| 1000°F (538°C) | 57 | 58.5 | 59.5 | 60.5 | 61.5 | 62 |
| Freezer (-10°F after Plate/Oil Quench) | ||||||
| 300°F (150°C) | 61 | 62 | 63 | 63.5 | 64 | 64.5 |
| 350°F (175°C) | 59.5 | 60.5 | 61.5 | 62.5 | 63 | 63.5 |
| 400°F (205°C) | 58.5 | 59.5 | 60 | 61.5 | 62 | 62 |
| 500°F (260°C) | 58 | 58.5 | 59 | 60 | 60.5 | 61 |
| Liquid Nitrogen or Dry Ice after Plate/Oil Quench | ||||||
| 300°F (150°C) | 60.5 | 62 | 63 | 64 | 64.5 | 65 |
| 350°F (175°C) | 59.5 | 61 | 62 | 62.5 | 63.5 | 64 |
| 400°F (205°C) | 58.5 | 60.5 | 61 | 62 | 62.5 | 63.5 |
| 500°F (260°C) | 57.5 | 59 | 59 | 60 | 60.5 | 62 |
| 1000°F (538°C) | 56 | 59 | 60.5 | |||
| Vacuum Furnace – 2 Bar Quench | ||||||
| No Cryo | With Cryo | |||||
| Temper | 1950°F (1065°C) |
2050°F (1120°C) |
2150°F (1175°C) |
1950°F (1065°C) |
2050°F (1120°C) |
2150°F (1175°C) |
| 300°F (150°C) | 59.5 | 62 | 62.5 | 61 | 62.5 | 64 |
| 350°F (175°C) | 58.5 | 60.5 | 61.5 | 59 | 61.5 | 63 |
| 400°F (205°C) | 58 | 59.5 | 60 | 58.5 | 61 | 62 |
| 500°F (260°C) | 56.5 | 58 | 58.5 | |||
| 960°F (515°C) | 58.5 | 61 | 62 | |||
| Results may vary with hardening method and section size. | ||||||
Machinability and Grindability
In the annealed condition, CPM® MagnaCut is easier to machine than 20CV and S30V®. Similar grinding equipment and practices used for high speed steels are recommended. “SG” type alumina wheels or CBN wheels have generally given the best performance with CPM® steels.
Niagara Specialty Metals | 12600 Clarence Center Road, Akron, NY 14001


